Chronic renal failure cannot be cured, thus the goal of treatment is to slow down the progress of failure, reduce complications and control the symptoms. It is most important to control the underlying diseases, e.g.
diabetes mellitus,
hypertension, nephritis, etc. Patient should have regular follow-up; to strictly follow the medical advice with respect to diet, exercise and medications to control the condition.
Diet control
It is important for patients with chronic renal failure to follow appropriate diet control. Appropriately reduce the intake of protein can help to slow down the progress of renal failure. Patient should also limit the intake of potassium, phosphorus, sodium and water and control the cholesterol level.
Medications (Chinese version only)
Common medications include:
- Drugs to control blood pressure: e.g. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors) or Angiotensin II receptor blockers to protect kidney function.
- Erythropoietin to promote the formation of red blood cells.
- Vitamin D to support bone metabolism.
- Phosphate binder to lower the Phosphorus concentration in blood.
Renal replacement treatment
A patient cannot remove the accumulated waste products and excess water in the body when reaching end-stage of renal failure (only 10% to 15% capacity of kidney function left). Some form of kidney replacement treatment is required to survive, otherwise it may be fatal.
Kidney replacement treatments include:
Dialysis: currently, hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis are the two main kinds of dialysis treatment.
i) Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis - known as "cleansing of blood", is making use of a dialyser (artificial kidney) to remove excess water, electrolytes and the waste products from the blood. Blood is taken off the patient's body via a vascular access such as arteriovenous fistula (a connection made between an artery and a vein at the forearm) or a venous catheter inserted into a main blood vessel in the neck. The blood is circulated by a dialysis machine at around 200cc/min, passing through the artificial kidney to filter off the waste products and the excess fluid. The "cleansed" blood is then return to the patient. A patient may need 2 to 3 haemodialysis treatment per week and each treatment takes 4 to 6 hours. Hemodialysis can be performed at a dialysis centre or at home (in the evening) for those who are able to do so.
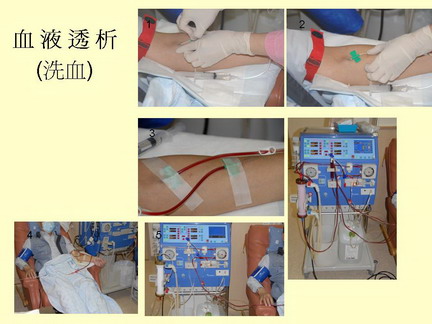
Advantages: quick, effective, only 2 to 3 treatments per week, an intermittent therapy.
Disadvantages: needs to go to dialysis center for the treatment, the treatment is only intermittently and is costly.
Centers where Hemodialysis services are provided:
- Renal Units of the Hospital Authority (for those who are not suitable for peritoneal dialysis)
- "Nocturnal haemodialysis at home support program" provided by the Hospital Authority together with Hong Kong Kidney Foundation Limited
- Haemodialysis centers organized by charitable organizations
- Haemodialysis centers of private hospital
ii) Peritoneal dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis - known as "cleansing the abdomen" is making use of the blood vessel on the peritoneum (a thin membrane that lines the inside of the abdomen and surrounds and supports the abdominal organs) which allows a dialysis process.
A peritoneal dialysis catheter is implanted into the patient's abdomen as a channel where the dialysis fluid can pass in and out. The infused dialysis fluid allow waste product to be diffused out from the body into the dialysis fluid and to remove the excess water from the body.
Peritoneal dialysis is performed at home and can be continuous or intermittent:
- Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis - CAPD
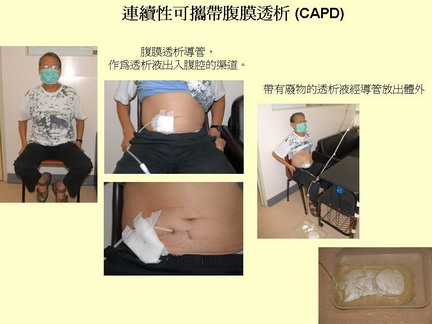
About 90% of patients in Hong Kong is making use of this method.
The dialysis treatment (exchange of the dialysis fluid) is performed at home. The dialysis fluid is instilled into the abdomen through an implanted catheter and the dialysis fluid is allowed to dwell inside the abdomen for 4 to 10 hours. During this time, the waste products diffuse into dialysis fluid. The dialysis fluid is then drained out from the body (with the waste product) after 4-10 hours and a new bag of dialysis fluid is then instilled into the abdomen again. This process is repeated 3-4 times per day.
Advantages: removing waste product and excess water continuously, less burden on the heart and the patient can have normal activity during the dialysis process.
Disadvantages: risk of peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum) from the fluid exchange, but this complication is low if the dialysis process is performed carefully.
- Automated Peritoneal Dialysis
The dialysis treatment is performed during sleep overnight by connecting up to an automated peritoneal dialysis machine before going to bed every night. The machine will automatically exchange the dialysis fluid every hour or so through out the night (for 10 to 12 hours).
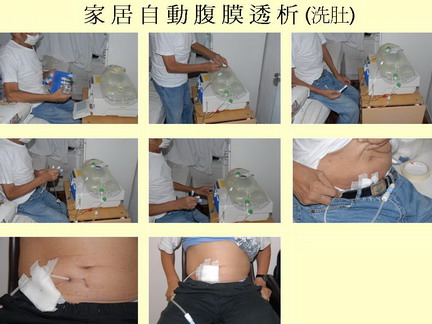
The advantages of peritoneal dialysis are that the patient can take care of himself/herself and the levels of toxin and water remain stable. Patient can maintain relatively normal social life and even work. There is an infection risk but this is low if the dialysis process is carried out carefully.
iii) Kidney transplant
It is a surgical transplant of a kidney from a donor to renal failure patient. The donor kidney could be from a dead (brain-stem dead) person or donated from a living person (family member). In 2016, 78 people underwent kidney transplant in Hong Kong (60 people with Renal from the dead and 18 people with kidney from living donors). There are about 2000 patients waiting for kidney transplant.
Kidney transplant is very successful:
Survival rate of patient in 1 year and 5 years: Kidney transplant from dead person- 95% and 89%; kidney transplant from living donors - 96% and 95%
Survival rate of kidney transplant in 1year and 5 years: Kidney transplant from dead body - 92% and 84%; kidney transplant from living donors - 94% and 89%
Kidney transplant surgery can cause complications, of which the most concerned one is "rejection". Patient has to take various medicines and be attentive to various nursing skills.